
Mandibular fracture – often bilateral occurring directly at the side of trauma, and indirectly at the contralateral side due to transmitted forces.Fractures affecting of maxillary bones are classified using the Le Fort classification, ranging from 1 to 3. Maxillary fracture – associated with high-energy trauma.There is often significant soft tissue swelling and associated epistaxis. Nasal fracture – the most common facial fracture, due to the prominent position of the nasal bones at the bridge of the nose.

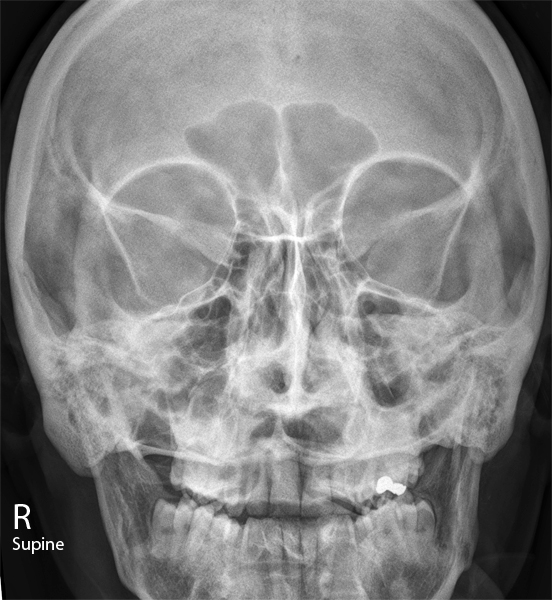
The four most common facial fracture types are:
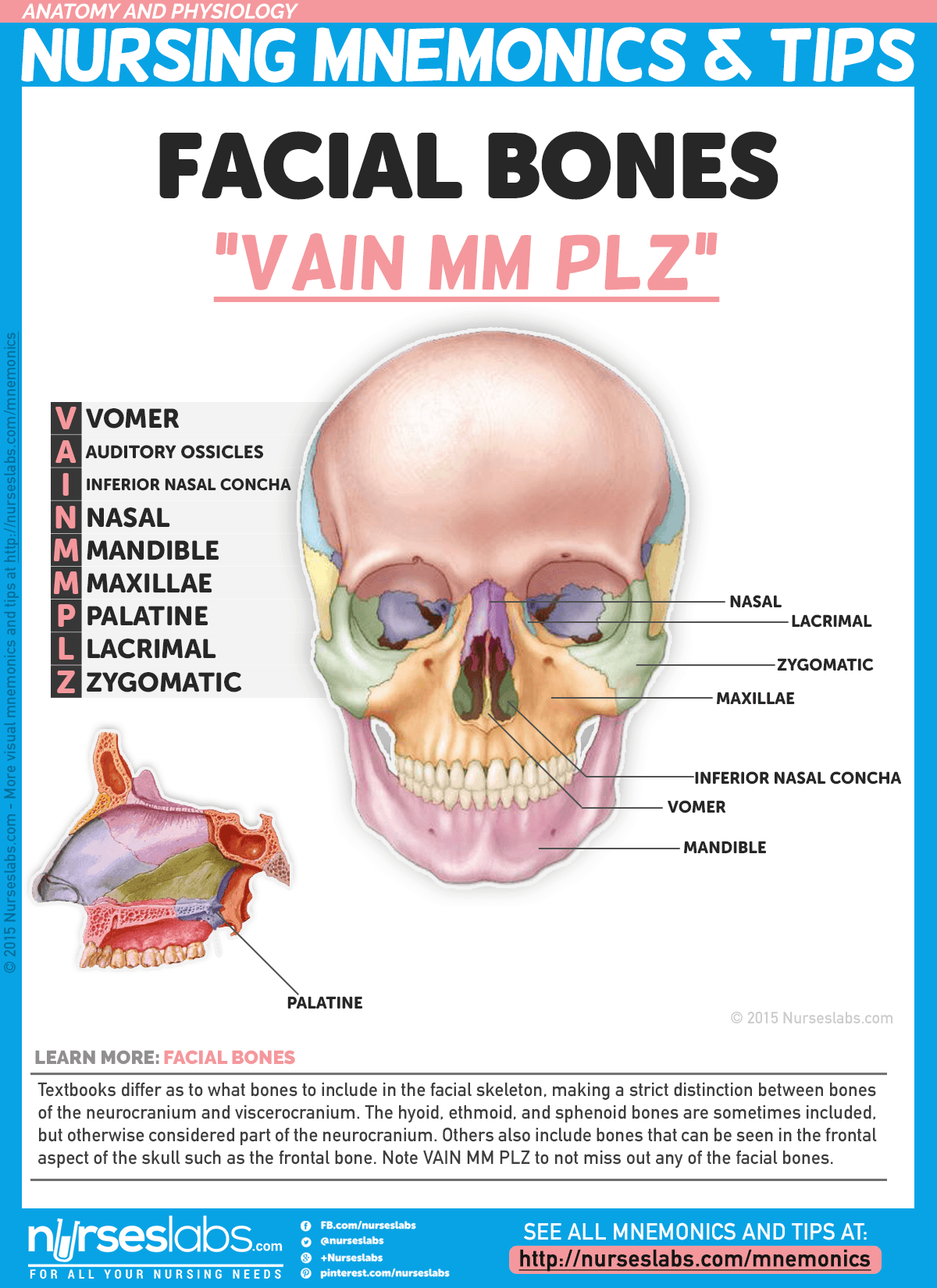
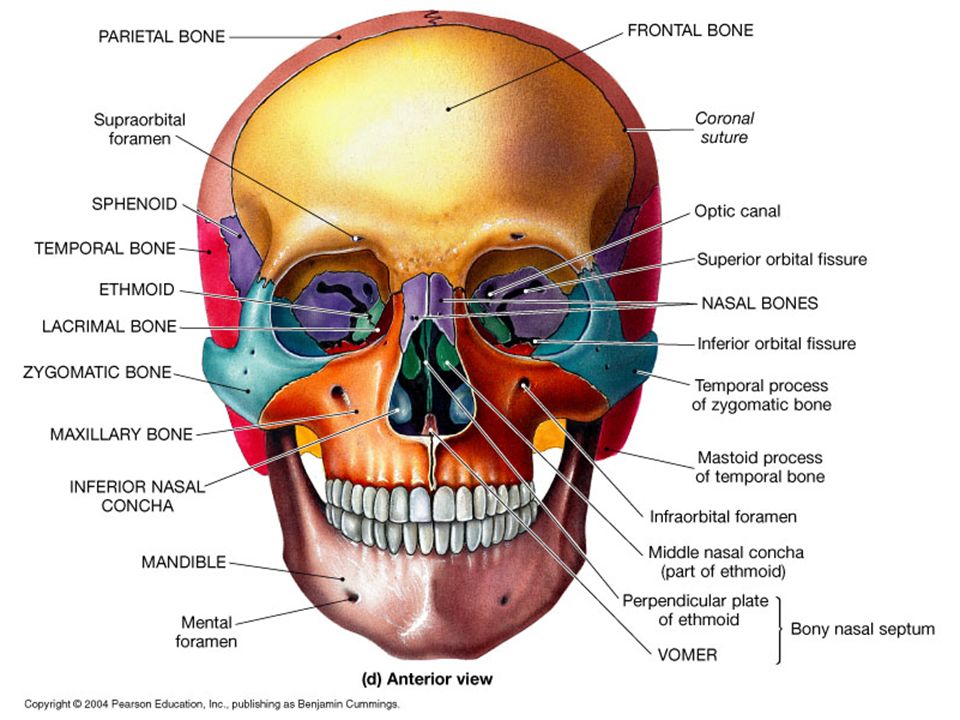
Zygomatic (2) – forms the cheek bones of the face and articulates with the frontal, sphenoid, temporal and maxilla bones.The frontal bone, typically a bone of the calvaria, is sometimes included as part of the facial skeleton. It consists of 14 bones, which fuse to house the orbits of the eyes, the nasal and oral cavities, and the sinuses. The facial skeleton (also known as the viscerocranium) supports the soft tissues of the face.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
